 |
Zsuzsa Bajtay Ph.D., D.Sc.Professor
E-mail: bajtay.zsuzsanna(at)ttk.elte.hu |
Short CV
- M.Sc.: biologist, 1984, Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest
- Ph.D.: Immunology, HAS/ELTE, 1996.
- Habilitation: 2010, ELTE
- D.Sc.: 2015, HAS
- professor: ELTE, 2016-
Postdoctoral activity
- 1996 (2 months), 2002-2004 (two years): Department of Hygiene, Microbiology and Social Medicine, Innsbruck Medical University and Ludwig Boltzman Institute for AIDS Research, Austria
Fellowships and awards
- Bolyai plaquette (2008.)
- János Bolyai Fellowship (2004-2006.)
- György Békésy Fellowship (2002.)
- Award of Lajos Kisfaludy Foundation (2001.)
- Award of Bio-Science (1998.)
- Award of Hungarian Society for Immunology (1996.)
Further activities
- Member of the Board of the Hungarian Society for Immunology (2010-)
- Member of the Committeee of Immunology at HAS (2011-)
Research interest
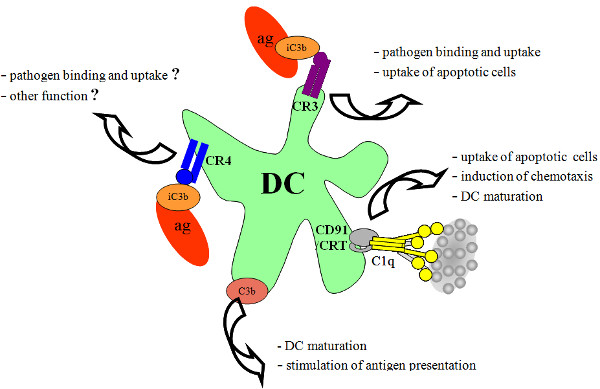
I focus on the role of complement on various functions of macrophages and dendritic cells. Dendritic cells are known to be important cellular participant of the immune response. These cells orchestrate several processes that are key to immune defense. The complement system is the major soluble component of the host defense against pathogens.
The major complement component C3 has been demonstrated to play key role during complement activation and the regulation of immune response as well. C3 can bind to different complement receptors present on the surface of immune cells, including dendritic cells. The deposition of the activated fragments of complement component C3 allows the binding of opsonized antigens to cells expressing various complement receptors. Dendritic cells, macrophages and neutrophil granulocytes express CR3 and CR4 complement receptors, that are members of the family of β2-integrins. Their similarity is very high regarding their extracellular domain; 87% respectively. The ligand specificity of CR3 (CD11b/CD18) and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) is highly overlapping, and their main ligand is the same: the iC3b fragment. However they differ in their intracellular domain and this suggests fundamental differences between the two receptors. The most important role of CR3 is the binding and phagocytosis of pathogens opsonized by iC3. Our results show that complement C3 dependent phagocytosis of human DCs is mediated mainly by CR3. The role of CR4 is not well characterized and little is known about its function on DCs. Our aim is to determine exact role and function of CR3 and CR4.
It has been published recently that primary human C3-deficiency results in an important functional defect of DCs. We examined how covalently fixed C3b influences maturation of DCs. Our results demonstrate that DCs are able to fix locally produced C3b which increases the capacity of these antigen presenting cells to stimulate T lymphocytes. The possible significance of our findings was strengthens by modeling the in vivo situation, where DCs and macrophages are in close vicinity in the peripheral lymphoid tissues.
Research projects
- Regulation of various functions of macrophages and dendritic cells by complement C3 and β2-integrins
- Differencies in the expression of CR3 and CR4 in the human system
- Function of CR3 and CR4 during endocytosis of pathogens by human phagocytes
- Distinct role of CR3 and CR4 in cellular adherence
Methods/Experience
- Human tissue culture and cell separation techniques (Ficoll gradient, magnetic bead technic), in vitro differentiation of blood cells
- Protein isolation methods (FPLC), Western-bloting method
- Detection of extracellular and intracellular molecules by ELISA-techniques, PCR, cytofluorimetry, confocal laser scanning microscopy, RNA silencing method
- Functional assays: cytokine production,( ELISA, ELISPOT), opsonization techniques and phagocytosis assays, antigen-presentation and cellular proliferation assays (CFSE)
Selected publications
- Zs. Bajtay, L. Kacani, A. Erdei, M.P. Dierich. HIV-1 induces human monocyte-derived macrophages to produce complement component C3 and to fix C3 on their surface. Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 1998. 63. 463-468.
- K. Kerekes, J. Prechl, Zs. Bajtay, M. Józsi, A. Erdei. A further link between innate and adaptive immunity: C3-deposition on antigenpresenting cells enhances the proliferation of antigen-specific T cells. International Journal of Immunology. 1998. 10. 1923-1930.
- Zs. Bajtay, M. Józsi, Z. Bánki, S. Thiel, N. Thielens, A. Erdei. MBL and C1q bind to distinct structures on lymphocytes and macrophages and mediate differential effects. European Journal of Immunology. 2000. 30. 1706-1713.
- M. Józsi, J. Prechl, Zs. Bajtay, A. Erdei. Complement receptor type 1 (CR1, CD35) mediates inhibitory signals in human B lymphocytes. Journal of Immunology. 2002. 168(6). 2782-2788.
- Zs. Bajtay, Speth C, Erdei A., Dierich MP. Cutting Edge: Productive HIV-1 Infection of Dendritic Cells via Complement Receptor Type 3 (CR3, CD11b/CD18). J Immunol. 2004. 173(8). 4775-8.
- Bajtay Z, Csomor E, Sandor N, Erdei A. Expression and role of Fc- and complement-receptors on human dendritic cells. Immunology Letters 104 (1-2): 46-52 Sp. Iss. SI April 2006.
- Kristóf Katalin, Anna Erdei and Zsuzsa Bajtay. Set a thief to catch a thief: Self-reactive innate lymphocytes and self tolerance Autoimmunity Reviews 2008 Feb;7(4):278-83.
- Erdei A, Isaák A, Török K, Sándor N, Kremlitzka M, Prechl J, Bajtay Z. Expression and role of CR1 and CR2 on B and T lymphocytes under physiological and autoimmune conditions Mol. Immunol. 2009 Sep;46(14):2767-73. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Review.
- Sándor N, Pap D, Prechl J, Erdei A, Bajtay Z. A novel, complement-mediated way to enhance the interplay between macrophages, dendritic cells and T lymphocytes Mol Immunol. 2009 Dec;47(2-3):438-48.
- Sándor N, Kristóf K, Paréj K, Pap D, Erdei A, Bajtay Z. CR3 is the dominant phagocytotic complement receptor on human dendritic cells. Immunobiology. 2013 Apr; Volume 218, Issue 4, April 2013, Pages 652-663.
- Orgovan N, Ungai-Salánki R, Lukácsi S, Sándor N, Bajtay Z, Erdei A, Szabó B, Horvath R. Adhesion kinetics of human primary monocytes, dendritic cells, and macrophages: Dynamic cell adhesion measurements with a label-free optical biosensor and their comparison with end-point assays. Biointerphases. 2016 Sep 1;11(3):031001. doi: 10.1116/1.4954789
- Sándor N, Lukácsi S, Ungai-Salánki R, Orgován N, Szabó B, Horváth R, Erdei A, Bajtay Z. CD11c/CD18 Dominates Adhesion of Human Monocytes, Macrophages and Dendritic Cells over CD11b/CD18. PLoS One. 2016 Sep 22;11(9):e0163120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163120. eCollection 2016.PMID: http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0163120
- Erdei A, Sándor N, Mácsik-Valent B, Lukácsi Sz, Kremlitzka M, Bajtay Zs. The versatile functions of complement C3-derived ligands. Immunological Reviews. The versatile functions of complement C3-derived ligands.Immunol Rev. 2016 Nov;274(1):127-140. doi: 10.1111/imr.12498. Review.

